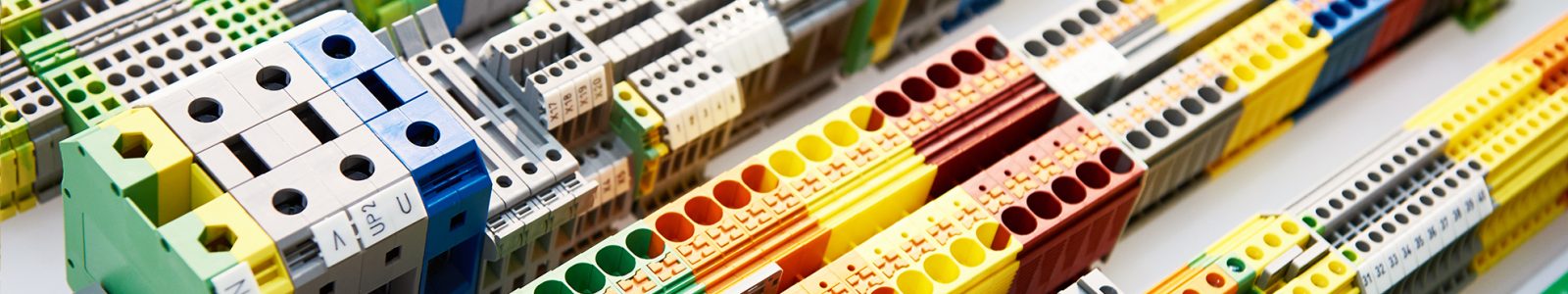
Terminal blocks join or terminate electrical wires. This is a simple but effective way of connecting wires. Other names for terminal blocks are connection terminals, terminal connectors and screw terminals.
The applications of terminal blocks are wide-ranging, but essentially they’re used wherever you need to connect electrical systems safely.
A terminal block has a modular housing. They are designed to secure and organise wire connections, but at the same time provide easy access to these connections for maintenance or for upgrading connections and systems.
In many electrical wiring systems, you’ll find multiple terminal blocks mounted on DIN rails.
The body of the terminal block is normally made of plastic or another insulating material. Terminal blocks come in different types, for use in different kinds of wiring system designs.
The number of poles in a terminal block equates to the number of circuits you can connect to the block.
Some blocks are double or even single-pole, while others can house as many as 24 poles.
Terminal blocks are direct mount, panel mount, free-hanging or PCB mount.
There are two main types of fittings in terminal blocks for securing wires:
Screw Terminal Blocks
Screw terminal blocks secure the wire they are connecting or terminating against the conductor with a tightened screw that closes the clamp.
Screwless Terminal Blocks
In screwless terminal blocks, the block secures the wire through the action of a spring clamp.
PCB Terminal Blocks
These types of terminal blocks are designed for use with printed circuit boards (PCBs). They mount onto PCBs.
As with other types of terminal blocks, these come with either screw or screwless fittings for wiring.
Types of Terminator Block Module
There are different designs of terminator block modules, enabling you to either use the blocks individually or have them interlock.
In single-piece blocks, the poles are contained in a single housing. In interlocking blocks, each block will have several poles and joined together you can create terminals with the capacity for multiple circuits.
Block Structure and Orientation
When designing systems with terminal blocks, there are certain mechanical considerations, in terms of the orientation of the blocks and the accessibility of connections.
To give you more flexibility, terminal blocks come in a range of structures and orientations.
Terminal block structures include:
- Single-feed – for simple wire to wire connections, with one input and one output contact on opposite sides of the block
- Double-level – two ascending levels of contacts, to increase the flexibility of circuits
- Three-level – three levels of contacts, and, like the double-level, these can be bridgeable.
There are three common orientations for terminal blocks:
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- 45°.
These orientations determine the wire entry on the terminal block. They’re useful when working with a design that has certain physical restrictions.
Electrical Specifications
The type of terminal block you choose should match the voltage and current requirements of your system.
There are various electrical specifications in terminal block design you must therefore take into account.
- Voltage rating – the terminal block’s voltage rating should be higher than that of the system you’re applying it to.
- Current rating – this is a very important parameter when choosing your terminal block since operating at too high a current can cause overheating and damage to the terminal block. Ensure that the block’s current rating is at least 150% of the system’s maximum current.
- Pitch – this is the distance from one pole to the next on the terminal block, and the terminal block’s overall rating may determine this.
- Pole count – the number of individual circuits the terminal block can house.
- Wire size or type – the wires need to physically fit into the block, so you should match the type of wire you intend to use with the terminal block’s specified wire size.
How to Choose Your Terminal Block
There are plenty of choices when it comes to terminal blocks, and you should consider your system design and how you want your terminal blocks to function in it.
The best way to approach this is in two stages:
- Select your terminal block type, including the type of mount and whether you want this to be screw or screwless
- Match the terminal block type to your system specifications, including voltage, current and maximum wire size.
If you want help and advice choosing the right terminals and connectors for your applications, please contact us.